
IS My Privacy Secure? How To Assure That When Visiting Websites?

Learn more about SSL/TLS certificate protocol, HTTPS, web errors, and how to assure that the web site which visited is working to your privacy secure
Mostly, What worries us, when we using websites and we ask ourselves constantly… IS my privacy secure?
Have you ever noticed that, some URLs begin with http://, while others begin with https://?
Also, you may have noticed these additional “errors” when browsing websites that require providing sensitive information, such as when to pay bills online or shopping online.
But, where did these additional “elements” come from? and, what do they mean?
Simply, the additional “s” means that your connection to this website is secure and encrypted, and any data that you shared with this website, will be secured. The technology that powers these little “s” is called SSL/TLS certificates, which stands for “Secure Sockets Layer“.
So, as a consumer, you always want to see https:// when visiting any website, and assure that your information and privacy are safe.
And, if you are a marketer or developer, you’ll need to sure you have an SSL/TLS or two for your audience, and also growth your business by saving your customers privacy.
After reading this article, you will find the answers of below questions:
- Is my privacy secure with SSl / TLs Certificate?
- What does an SSL/TLS Certificate contain?
- Why are we need an SSL/TLS certificate?
- How does SSL/TLS certificates works? What the is my privacy secure?
- Why am I facing website connection error?
- Why do websites need an SSL/TLS certificate?
- How do know if I need to confirm the existence of an SSL/TLS certificate for a site?
- How do I make sure I have an SSL/TLS certificate for a site?
- Does SSL/TLS work for email? Is my privacy secure when using my email?
- What are the types of an SSL/TLS certificate?
- How does a website obtain an SSL/TLS certificate?
“I cherish my privacy, and woe betide anyone who tries to interfere with that”
Jeff Beck – an English rock guitarist
1. Is my privacy secure with SSl / TLs Certificate?

Usually, browsers and web servers are share data in plain text, which leaving you vulnerable to eavesdropping. If an attacker is able to intercept all the data that is being sent between the browser and the web server, he can obtain this information and hacking your privacy. So, SSL/TLS Certificates allow to transfer sensitive information securely such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and login credentials.
SSL secures the data of millions of people on the Internet every day. Especially, during online transactions, or when sending confidential information. Internet users have come to associate their online security with the padlock code, which that comes with an SSL secured website, or the green address bar, that comes with an SSL secured website for extended verification. Also, SSL secured websites start with HTTPS instead of HTTP.
In a nutshell, the SSL/TLS certificate secure the website, and allows you to check your transactions, and information on the website with this certificate.
“Why are people preoccupied with people’s affairs, someone is preoccupied with the privacy of his brother, and there is a lot to occupy him”
Ahmed Shawky – an Egyptian poet and dramatist
2. What does an SSL/TLS Certificate contain?
As per below, SSL certificate contain the following information:
- The name of the domain. (which the certificate was issued for)
- The certificate holder’s name. (The person, organization, or device to which it is issued)
- The certification authority which issued it.
- The certificate’s serial number, issued date and expiration date.
- A copy of the certificate holder’s public key. (the private key is kept secret)
- The digital signature of the certificate-issuing authority.
- Associated subdomains.
Also, an SSL/TLS certificates are using public and private keys, which are basically long strings of characters used to encrypt and decrypt data.
Note that, data encrypted with a public key can only be decrypted with the private key and vice versa.
“I’m low-key. I like my privacy”
Kemba Walker – an American professional basketball player
3. Why are we need an SSL/TLS certificate? How is my privacy secure with SSL/TLS Certificates?
The first and last benefit of an SSL/TLS certificates is data encryption. Encryption is performed for communication between the browser (client), and the server through a special protocol, and the function of this protocol is to block this information from anyone than the user himself and the server, using a specific code. And by this way, your privacy had secured.
For instance, on Facebook website, and when login, you typing the username (User) and password (123456), and the server receives it in this way, Username (5A55aS51deSW) and password (A4S8W6R9D5Q4E8). Therefore, it is now in a state of complete encryption, which makes it difficult to decrypt this data.
In conclusion, The site that uses the SSL encryption feature is safe, but the site that doesn’t use the SSL encryption service, it’s sent and received data at a high risk of privacy hacking.
“Not to interfere in the privacy of others does not diminish your life, nor does it take from your balance, and there is no dragon after it to eat you, you just have to live for yourself and leave people to the Lord of people”
Unkown
4. How does SSL/TLS certificates works? What the way is my privacy secure?
- The browser communicates with a web server (website) that is secured by SSL/TLS Certificate (HTTPS).
- The browser request from the server to identify itself.
- The server sends a copy of its SSL/TLS certificate, including the server’s public key.
- The browser checks the certificate root against the list of trusted certification authorities, that the certificate is not expired, not revoked, and that its common name is valid for the website, which connects to. If the browser trusts the certificate, it creates a symmetric session key, encrypts it, and send it back using the server’s public key.
- The server decrypts the symmetric session key with its private key, and sends an encrypted acknowledgment, using the session key to initiate the encrypted session.
- The server and browser now encrypt all data sent using the session key.
This simply means that, anyone can put data in the box and close it, and only the server opens this box. Thus, the data transfer process has become very secure.
“The Internet is a worldwide platform for sharing information. It is a community of common interests. No country is immune to such global challenges as cyber-crime, hacking, and invasion of privacy”
Lu Wei – a Chinese politician
5. Why am I facing website connection error?
Are if neglecting this error? is my privacy secure?
An SSL/TLS communication error occurs, when the page being accessed contains some security issues. Therefore, it happen to protect users, and cut-off access, to inform them that, there might be some security concerns, if they come forward.
They can take a number of forms and are often different by browser. In some cases, the page might turn red with https:// also highlighted in red. With Google Chrome, there are a number of messages that users may see appearing on their screen. These include “Your connection is not private” or simply “This web page is not available”.
This could be the result of an outdated security code on the website, and it doesn’t necessarily mean that the site being accessed is suspicious. But users should take connection errors seriously. Especially, if they are not 100% sure of the destination website.
While there are ways to get around SSL/TLS connection errors, it is recommended that users not do so.
“Half of rest is not interfering with other people’s lives, half of politeness is non-interference in what is not your concern”
Unknown
6. Why do websites need an SSL/TLS certificate? How saving our privacy to be secured?
The website needs an SSL/TLS certificate to keep user data safe, verify website ownership, prevent attackers from creating a fake copy of the site, and gain user trust.
Encryption: SSL / TLS encryption is enabled due to the association of public and private keys facilitated by SSL/TLS certificates. Clients (like web browsers) obtain the public key needed to open the TLS connection from the server’s SSL certificate.
Authentication: SSL/TLS certificates verify that the client is talking to the correct server, that actually owns the domain. This helps prevent domain spoofing and other types of attacks.
HTTPS: Most importantly for businesses, an SSL certificate is necessary for a HTTPS web address. HTTPS is more secure than of HTTP, and HTTPS sites are websites whose traffic is encrypted by SSL / TLS.
In addition to securing user data in transit, HTTPS makes websites more reliable from a user’s perspective. Not many users will notice the difference between http:// and https:// web address, but most browsers have begun marking HTTP sites as “unsafe” in more obvious ways, in an effort to provide an incentive to switch to HTTPS and increase security.
“When it comes to privacy and accountability, people always demand the former for themselves and the latter for everyone else”
David Brin – an American scientist and author of science fiction
7. How do know if I need to confirm the existence of an SSL/TLS certificate for a site?
Basically, If you are going to enter your personal information on a website, such as names, addresses and credit card numbers, then you definitely need to make sure that the website have an SSL/TLS certificate to secure and protect your privacy. If you are not sure that, the website has this certificate, we advise you to be careful and don’t give your personal information, or your credit cards to this website, so that you aren’t exposed to your information being leaked or credit card being stolen.
But, don’t worry, and to be more reassuring, the Google search engine has modified the algorithm and mechanism of the search machine, and has given importance to the SSL/TLS certificate and has become part of the search engine. Started from July 2018. In additional, the Google Chrome web browser began treating any site without an SSL/TLS certificate as insecure. As a result, this action will reduce the ability of sites to appear in search results. Therefore, the use of an SSL/TLS certificate is no longer an option. And, became a basic requirement for all websites and blogs.
“Whoever avoids interfering in the privacy of others is a person who tends to calm and is averse to problems and negative people, and prefers to get things done simply, so beware of fabricating problems with the owner of this personality because he is ready to leave and stay away from everyone who tries to shake the stability of his life, because by his nature he escapes from problems so do not bring them to him”
Unknown
8. How do I make sure I have an SSL/TLS certificate for a site? How assure that is my privacy secure in this website?
There are some signs shown on every website pages, to assure that this website is saving your privacy. And, should be check it for every website during visiting to avoid hacking of your privacy.
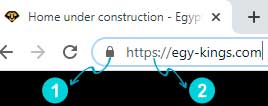
For Desktop Devices

For Mobile Devices (Android 10)
First: As per shown above, the browser shows a lock sign. (Where the lock sign appears varies from browser to browser)
Second: You can check the upper left corner of the address bar of your web browser. (As shown in above pic)
Have you ever noticed that before, all websites addresses begin with http:// or https://?
AS per mentioned before, the letter “S” written after HTTP, indicates that this site has an SSL/TLS certificate.
And, if the letter “S” isn’t present, this means that the website doesn’t carry it, and recommended to leave this website immediately, and be-careful when dealing with.
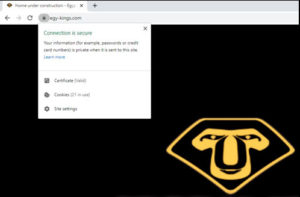
Desktop Devices
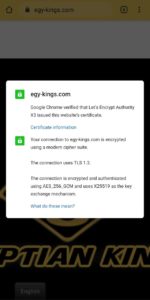
For Mobile (Android 10)
Third: As per shown above, When you click on the lock sign in the Google Chrome browser (the method differs from one browser to another), a phrase will appear to you, which indicating that this website is safe or if there is a problem.
Fourth: When you click on Certificate on Google Chrome (the method varies from browser to browser), the details of the website’s certified SSL/TLS certificate will appear to you.
As shown in the following picture:

Desktop Devices
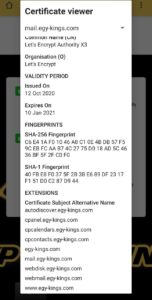
For Mobile (Android 10)
Also, there are more signs and visual indications that vary, which depending on the type of certificate which used.
“Privacy is not something that I’m merely entitled to, it’s an absolute prerequisite”
Marlon Brando – an American actor and film director
9. Does SSL/TLS work for email? Is my privacy secure when using emails?
Most of the major email providers use SSL/TLS encryption to encrypt users’ mail. In most cases, the SSL/TLS option will be checked automatically in the email settings. To retrieve mail that reported an error message, the user might have to deselect this option.
If the account where the users fetch mail supports SSL/TLS, therefor you can select this option to send data over a secure connection.
However, if a company is setting up its own email service. So, the IT team may need to verify that their provider is also secured by SSL/TLS. And, this action will eliminate security issues, when sending individual mail and mail shots.
“Whoever interferes with what does not concern him, will receive what he does not like”
Ancient Arab wisdom
10. What are the types of an SSL/TLS certificate?
There are several different types of SSL certificates. In this section, we will show them, As per, A single certificate can apply to one or multiple sites, depending on the type:
10.1. Single domain:
In this type, a single domain SSL/TLS certificate applies to only one domain. (“domain” is the name of a website, such as www.egy-kings.com)
10.2. Wildcard SSL certificate:
It is the most popular type among issuers of SSL or TLS certificates, providing complete site security.
This type of certificate coded with an asterisk (*), which is the type responsible for securing the entire domain. As well as, any subdomain of it.
As per this type, allows to secure the domain and all subdomains with a single certificate.
For example, a wildcard certificate could cover www.egy-kings.com, blog.egy-kings.com, and mail.egy-kings.com. While, a single-domain certificate could only cover the first domain.
10.3. Multiple Domains:
As the name indicates, multi-domain SSL/TLS certificates can apply to multiple unrelated domains.
Also, SSL certificates come with various verification levels.
As per, the level of validation is similar to a background scan, and the level changes depending on the accuracy of the scan.
10.4. Domain Validation SSL/TLS Certificates (DV):
This type of certificate is considered the most common used on the websites, all over the world. It is primarily used to verify the authenticity of the domain ownership of the person claiming it. All a business has to do is prove they control the domain.
10.5. Organization Validation SSL/TLS Certificates (OV):
This type of SSL certificate is preferred by some companies. As per, the business name appears in the certificate details, and gives more security, and it is better than the previous type of domain only.
This type of certificates depends on confirming the ownership of a specific institution. Therefore, when requesting this type of certificates, the organization documents house or documents proving their ownership of the company or institution.
This type of e-commerce is uncommon, as it is limited to use by companies and large stores to some extent.
Note that, this is the same type of testimonial that Google and Amazon use.
10.6. Extended Validation SSL/TLS Certificates (EV):
This type is the most unique, and has the highest levels of security and confidence. Therefore, It’s preferred to use for large economic entities, or giant service providers, such as international contracting companies and banks, as there are many fraudsters trying to impersonate these entities.
You can easily notice this type, unlike the previous ones. You not only see the lock sign, but you will also notice the name of the company or entity next to the lock as well, and the name gives more confidence to visitors. So, for this reason, those economic entities pay a larger amount to obtain this distinctive type of SSL/TLS certificates, to be eligible for this certificate. Therefor, the company owner submits the necessary business documents to prove the existence of his business.
“It’s dangerous, when people are willing to give up their privacy”
Noam Chomsky – an American linguist, philosopher
11. How does a website obtain an SSL/TLS certificate?
For an SSL/TLS certificate to be valid, domains need to obtain it from a certification authority (CA). And, this certification authority (CA) is an external organization (a trusted third party), that creates and issues SSL certificates. Also, the certification authority will sign the certificate digitally with its private key. Therefore, allowing client devices to verify it. Most, but not all, CAs will charge a fee to issue an SSL certificate.
Once issued, the certificate must be installed and activated on the website’s original server. Usually, Web hosting services can handle this for website operators. Once activated on the originating server, the website will be able to load over HTTPS, and all traffic to and from the site will be encrypted and secured.
“Most intruders, suffer from weak religious, cultural and moral integrity in their personal characteristics”
Najwa Al-Tamimi – an Arabic Social Worker
Finally
We recommended that, you should be don’t shop or enter your information to website, before assure that it have SSL/TLS Certificate, for securing your privacy.
References: Godaddy / Digicert / Cloudflare / Websecurity / Hubspot / Servawy / Afhmseo / Alrab7on / Arabtechnologie
Related Posts
How Can Be SSL Securing My Privacy From Hackers?
Shopping Online? How To Get Happy Shopping And Pay Safely?






You must be logged in to post a comment.